基本力反馈教程
本教程将指导您创建一个包含刚度和阻尼的基本触觉模拟,模拟与球体等静态物体接触的物理特性。 本教程结束时,您将获得一个模拟,可以感受球体的存在,并调整其硬度和阻尼属性,获得不同的触觉体验。
导言
本教程的核心挑战是开发一个函数,能够计算与具有刚度和阻尼的球体接触时产生的力。 在这种情况下,刚度的作用就像弹簧一样,越压缩产生的力越大。 而阻尼则代表物体的运动阻力,移动速度越快,阻力越大。
场景设置
首先,按照以下步骤设置触觉装备 入门指南确保 触觉起源的位置、旋转和缩放设置为 (0, 0, 0) 和 (1, 1, 1) 分别是
然后,创建一个名为 Sphere 具有以下特性
- 职位:
(0, 0, -0.1)(设备前方约 10 厘米处)。 - 规模:
(0.2, 0.2, 0.2)(相当于一个直径 20 厘米的球体)
力反馈脚本
添加一个新的 C# 脚本到 球体 名为 SphereForceFeedback.cs.
该脚本将计算Inverse3 光标与球体接触时所受的力,同时考虑到刚度和阻尼。
用以下属性初始化脚本:
[SerializeField]
private Inverse3 inverse3;
[Range(0, 800)]
public float stiffness = 300f;
[Range(0, 3)]
public float damping = 1f;
private Vector3 _ballPosition;
private float _ballRadius;
private float _cursorRadius;
只有当光标穿透球体时,力的计算才会发生,从而模拟触摸具有确定刚度和阻尼的实物的感觉。
力的计算 ForceCalculation 方法将负责这一工作,同时考虑光标的位置和速度:
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Apply damping based on the cursor velocity
force -= cursorVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(Inverse3 device)
{
// Calculate the ball force
var force = ForceCalculation(device.LocalPosition, device.LocalVelocity,
_cursorRadius, _ballPosition, _ballRadius);
device.CursorSetLocalForce(force);
}
在 Awake 方法,初始化 _ballPosition, _ballRadius和 _cursorRadius 来设置场景数据:
private void SaveSceneData()
{
var t = transform;
_ballPosition = t.position;
_ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Model.transform.lossyScale.x / 2f;
}
private void Awake()
{
SaveSceneData();
}
确保注册和取消注册 OnDeviceStateChanged 中的回调 OnEnable 和 OnDisable 方法,以正确处理交互过程中的力反馈:
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
游戏体验
按住Inverse3 光标,进入 "播放 "模式并尝试触摸球体。 您应该能够感受到球体的存在,并通过 Unity 检查器操作其刚度和阻尼属性,从而获得与虚拟对象进行交互的真实感。
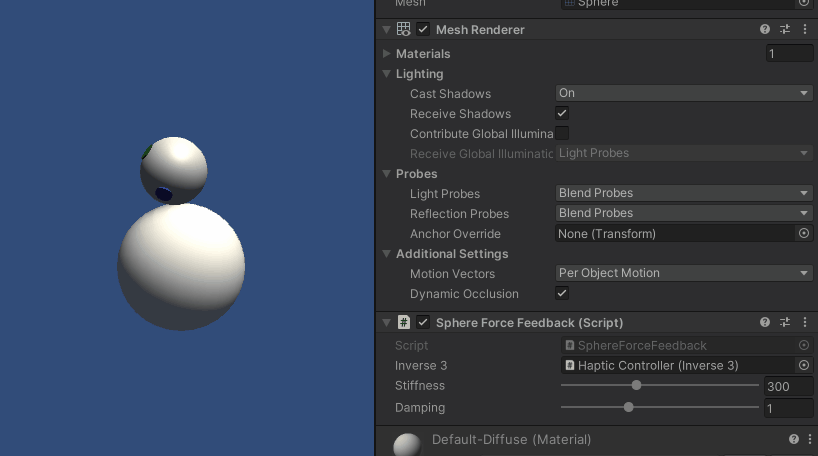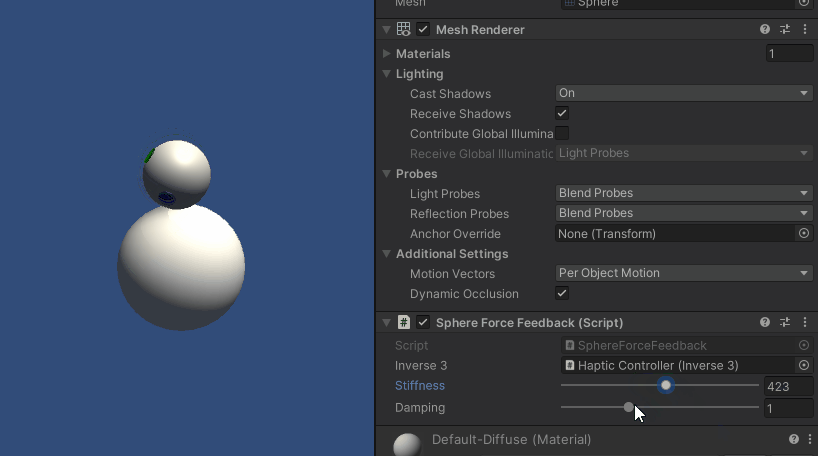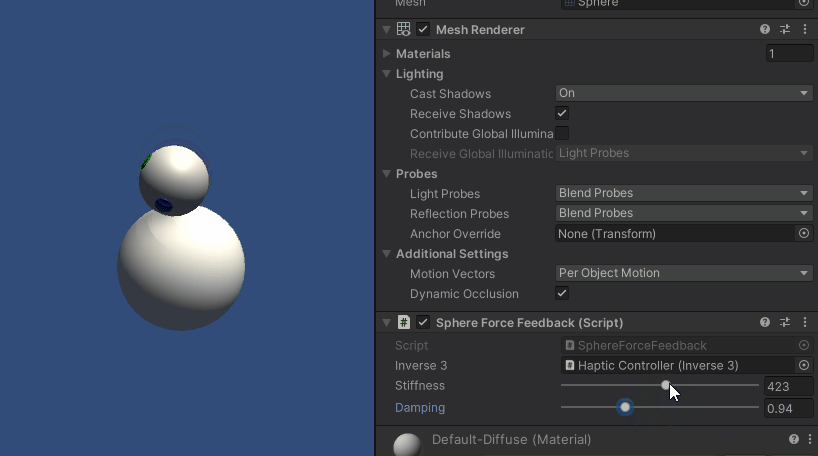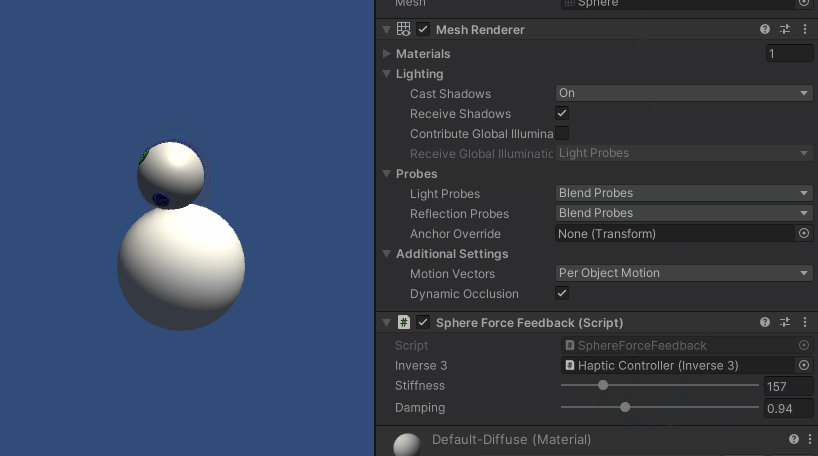
源文件
本示例的完整场景和所有相关文件均可从 Unity 软件包管理器中的教程示例中导入。
SphereForceFeedback.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using Haply.Inverse.Unity;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._2_BasicForceFeedback
{
public class SphereForceFeedback : MonoBehaviour
{
// must assign in inspector
public Inverse3 inverse3;
[Range(0, 800)]
// Stiffness of the force feedback.
public float stiffness = 300f;
[Range(0, 3)]
public float damping = 1f;
private Vector3 _ballPosition;
private float _ballRadius;
private float _cursorRadius;
/// <summary>
/// Stores the cursor and sphere transform data for access by the haptic thread.
/// </summary>
private void SaveSceneData()
{
var t = transform;
_ballPosition = t.position;
_ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Model.transform.lossyScale.x / 2f;
}
/// <summary>
/// Saves the initial scene data cache.
/// </summary>
private void Awake()
{
SaveSceneData();
}
/// <summary>
/// Subscribes to the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unsubscribes from the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the force based on the cursor's position and another sphere position.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cursorPosition">The position of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorVelocity">The velocity of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorRadius">The radius of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="otherPosition">The position of the other sphere (e.g., ball).</param>
/// <param name="otherRadius">The radius of the other sphere.</param>
/// <returns>The calculated force vector.</returns>
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Apply damping based on the cursor velocity
force -= cursorVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler that calculates and send the force to the device when the cursor's position changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="device">The Inverse3 device instance.</param>
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(Inverse3 device)
{
// Calculate the ball force
var force = ForceCalculation(device.LocalPosition, device.LocalVelocity,
_cursorRadius, _ballPosition, _ballRadius);
device.CursorSetLocalForce(force);
}
}
}