基本力和位置教程
本指南提供了一个施加力和可视化Inverse3 光标移动的简单演示。 最后,Inverse3 将模拟被虚拟橡皮筋拴在起始位置的感觉,同时球形 GameObject 将显示光标的位置。
导言
入门指南》介绍了 Inverse3对象、其功能以及生成恒力的方法。 我们这里的目的是模拟光标上的橡皮筋效应。橡皮筋的行为类似于弹簧,这意味着它的力受其两端点之间的刚度和距离的影响。 因此,我们的目标是设计一个函数,在给定位置和刚度的情况下,产生一个力,使光标抵制远离原点的移动。
场景设置
通过GameObjects >Haply菜单创建触觉装配(一只手)。
力和位置组件
选择 触觉起源 游戏对象,并添加一个名为 ForceAndPosition.cs 并填充 ForceAndPosition 类,代码如下
[SerializeField]
private Inverse3 inverse3 = null;
[SerializeField, Range(0, 400)]
private float stiffness = 100;
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the force.
var force = (inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition - inverse3.CursorLocalPosition) * stiffness;
// Apply the force to the cursor.
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
该段将刚度设置为 100 牛顿/米(N/m),模拟相对较软的弹簧。
它还引入了 inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition返回工作区中心的属性。
该方法通过从工作区中心减去光标的位置来计算力,然后将计算结果乘以刚度。
最后,使用 inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce.
纳入 OnDeviceStateChanged 中的回调 OnEnable 和 OnDisable 方法,详见 入门指南:
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
游戏玩法
按住Inverse3 光标,激活 "播放模式",并尝试操纵设备。您会发现光标移动会产生一个力。 光标离起始位置越远,这种力就越明显。
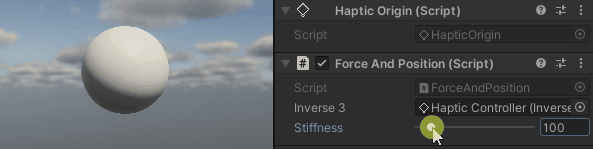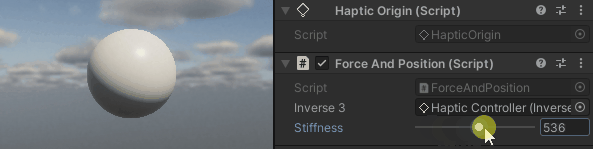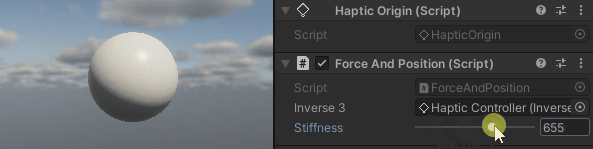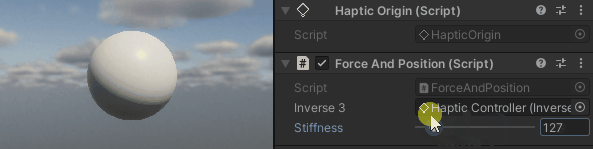
源文件
本示例使用的最终场景和所有相关文件都可以从 Unity 软件包管理器中的教程示例中导入。
ForceAndPosition.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceControllers;
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceData;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._1_ForceAndPosition
{
/// <summary>
/// Demonstrates the application of force to maintain the cursor at its center position.
/// </summary>
public class ForceAndPosition : MonoBehaviour
{
public Inverse3Controller inverse3;
[Range(0, 400)]
// Stiffness of the force feedback.
public float stiffness = 100;
private void Awake()
{
inverse3 ??= FindObjectOfType<Inverse3Controller>();
}
/// <summary>
/// Subscribes to the DeviceStateChanged event when the component is enabled.
/// </summary>
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unsubscribes from the DeviceStateChanged event and reset the force when the component is disabled.
/// </summary>
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
inverse3.Release();
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler that calculates and send the force to the device when the cursor's position changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">The Inverse3 data object.</param>
/// <param name="args">The event arguments containing the device data.</param>
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the force.
var force = (inverse3.WorkspaceCenterLocalPosition - inverse3.CursorLocalPosition) * stiffness;
// Apply the force to the cursor.
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
}
}